Reduce the number of MySQL connections with persistent connections in PHP singleton mode
In the Mysql-driven PHP website, MySql connections are generally released by the end of the script, in some hierarchical PHP websites, if a page contains multiple data access classes, because each data access class will have a database connection, resulting in this page before the end of the script will have multiple database connections, in some large page connections may be as many as tens or hundreds, for this need to need the necessary control, for the interpreted PHP language, the script is executed sequentially, That is to say, the use of database connection is only one at the same time, according to this feature, it can be modified with a singleton mode.
<?php
class Config1 {}
class Config
{
/*
* You must first declare a static private property: the instance that holds the current class
* 1. Why does it have to be static? Because static members belong to the class and are shared by all instances of the class
* 2. Why does it have to be private? Direct external access is not allowed, only methods are controlled through class methods
* 3. Why should there be an initial value of null, because the internal provider of the class needs to detect the state of the instance and determine whether it needs to be instantiated
*/
private static $instance = null;
//Save the user's custom configuration parameters
private $setting = [];
//Constructor privatization: Instantiation from outside the class is prohibited
private function __construct(){}
//Cloning method privatization: Prohibit external cloning of objects
private function __clone(){}
//Because class instances are returned with static properties, static properties can only be used in static methods
//So you must create a static method that generates a unique instance of the current class
public static function getInstance()
{
//Detects whether the current class property $instance has saved an instance of the current class
if (self::$instance == null) {
//If not, an instance of the current class is created
//self::$instance = new self();
self::$instance= new mysqli(DB_SERVER, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD, DB_NAME);
self::$instance->set_charset('utf8');
}
//If you already have the current class instance, return it directly, do not create the class instance repeatedly
return self::$instance;
}
//Set configuration items
public function set($index, $value)
{
$this->setting[$index] = $value;
}
//Read the configuration item
public function get($index)
{
return $this->setting[$index];
}
}
//Instantiate the Config class
$obj1 = Config::getInstance();
$obj2 = Config::getInstance();
var_dump($obj1,$obj2);
$obj1->set('host','localhost');
echo $obj1->get('host');Of course, in this code, the connection information such as the account number and password of the database is hard-coded, and the corresponding information can be injected by modifying the GetConnec() function.
With this script, you can control only one database connection to a page. This reduces the number of MySQL connections. However, although the number of connections for a single request is reduced, if this page is refreshed multiple times, it will still produce a large number of MySQL connections and reduce performance, as shown in the figure, after the page is refreshed multiple times, the number of MySQL connections appears a lot.

How to solve a large number of connections in the case of multiple refreshes, the answer is to use mysql long connection;
We put the above code
$connec=mysqli_connect(“127.0.0.1”, “root”, “root”); Database address, password, etc
Changed to
$connec=mysqli_connect(“p:127.0.0.1”, “root”, “root”); Database address, password, etc
Note: The above code adds a “p:” prefix before the IP address, indicating that the mysql persistent connection is used, after the modification is completed, we refresh the page several times.
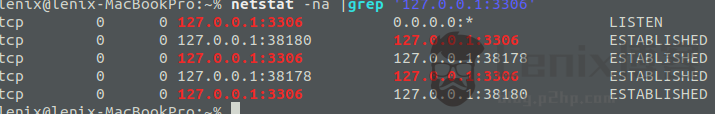
As shown in the picture above, only 2 are connected. Resolve successfully.
Of course, in addition to using MySQL’s persistent connection, you can also modify the connection reuse parameters of Linux kernel parameters, which can also achieve the goal.
Using MySQL persistent connections can greatly improve performance, so be sure to use MySQL persistent connections.

Leave a Reply